Ankle Pain: Causes, Symptoms, Treatments and Prevention.
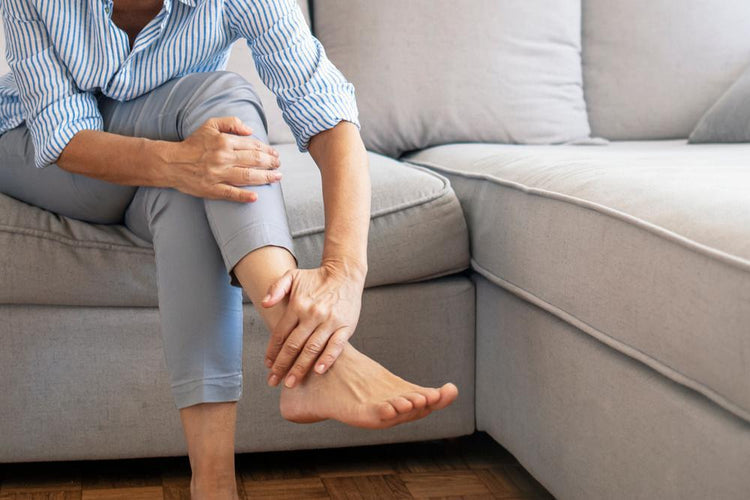

Ankle pain is a common problem that can be caused by a variety of factors. The ankle joint is a complex structure that is made up of bones, ligaments, tendons, and muscles. It is also one of the most frequently used joints in the body and is therefore susceptible to injury and wear and tear. Some common causes of ankle pain include sprains, fractures, arthritis, tendonitis, and bursitis. Other causes can include nerve problems, gout, and infections. In some cases, the pain may be referred from other parts of the body, such as the knee or hip. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience persistent or severe ankle pain, as prompt treatment can help prevent further damage and promote healing.
Ankle pain is a common issue that affects people of all ages, genders and activity levels. The ankle is a complex joint that is prone to injury and can be subject to various causes of pain. Some of the most common causes of ankle pain include sprains, fractures, tendinitis, bursitis and arthritis.

Ankle Sprain:
Ankle sprains are common injuries that occur when the ligaments in the ankle are stretched or torn. The ligaments are strong bands of tissue that connect the bones in the ankle and help to stabilize the joint. When these ligaments are damaged, the ankle becomes unstable and can cause pain, swelling, and difficulty in walking or moving.
Ankle sprains can occur in various ways. The most common cause is twisting the ankle while walking, running, or jumping. This can happen when the foot turns inward or outward and the ligaments on the outside or inside of the ankle are stretched or torn. The risk of spraining the ankle is higher for individuals who engage in sports that require quick movements, jumping, or change of direction.
The symptoms of an ankle sprain may vary depending on the severity of the injury. Mild sprains may cause pain and swelling, but the person can still walk or bear weight on the affected ankle. Moderate sprains may cause more significant pain, swelling, and bruising, and the person may not be able to walk or bear weight on the ankle. Severe sprains may cause intense pain, swelling, bruising, and difficulty in moving the ankle. In some cases, a severe sprain can also cause a bone fracture.
Diagnosis of an ankle sprain is usually made by examining the affected area and taking a medical history. X-rays or MRI scans may also be ordered to confirm the diagnosis and determine the severity of the injury.
The treatment of an ankle sprain depends on the severity of the injury, but there are several common approaches that can help to reduce pain and promote healing.
The first step in treating an ankle sprain is to reduce swelling and inflammation. This can be done by applying an ice pack to the affected area for 20-30 minutes at a time, several times a day. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen, can also help to reduce swelling and relieve pain.
In the case of a mild sprain, rest and immobilization of the affected ankle may be all that is needed to promote healing. This can be achieved through the use of a brace or wrap, which helps to stabilize the ankle and prevent further injury. Physical therapy or exercises to improve flexibility and strength may also be recommended.
In more severe cases, a doctor may recommend more intensive treatment, such as a cast or crutches. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair damaged ligaments or to correct any underlying problems that may have contributed to the injury.
Regardless of the severity of the injury, rehabilitation is an important part of the recovery process. This may involve physical therapy, exercises to improve range of motion and strength, and gradual return to normal activities, such as walking and running.
It is also important to take steps to prevent ankle sprains from reoccurring in the future. This may include wearing appropriate footwear and braces, avoiding activities that put excessive strain on the ankle, and participating in regular exercises to improve balance and stability.
An ankle sprain can be a painful and debilitating injury, but with the right treatment and rehabilitation, it is possible to recover fully and prevent future sprains from occurring. Whether it is a mild sprain or a more severe injury, it is important to seek prompt and appropriate treatment to ensure the best possible outcome.
Fracture:
Ankle fractures are a common injury, with more than 1 million cases reported each year in the United States alone. They can occur in people of all ages and activity levels, from young children to elderly individuals. However, they are more common in athletes and people who engage in high-impact activities, such as basketball, soccer, or running. Ankle fractures are a common type of bone fracture, which occurs when one or more of the ankle bones break. The ankle is made up of three bones: the tibia, fibula, and talus. Ankle fractures can vary in severity, from a simple crack in the bone to a complete break, which can cause significant pain and immobility. In this article, we will discuss the symptoms, causes, and treatments for ankle fractures.
The symptoms of an ankle fracture may include the following:
Pain in the ankle joint, which can be severe
Swelling, tenderness, and bruising around the ankle
Inability to put weight on the affected ankle
Deformity or a visible misalignment of the ankle bone
Numbness or tingling in the foot or toes
Limited range of motion in the ankle joint
Ankle fractures can occur due to various reasons, such as:
Trauma: Ankle fractures are commonly caused by traumatic events, such as a fall, car accident, or sports injury.
Osteoporosis: In people with osteoporosis, the bones become weak and brittle, making them more susceptible to fractures.
Overuse: Overuse injuries, such as stress fractures, can also cause ankle fractures in athletes and people who engage in activities that put repetitive stress on the ankle.
The treatment for an ankle fracture depends on the severity of the fracture. In general, the goal of treatment is to stabilize the ankle, promote healing, and restore normal function. The treatment options for ankle fractures include:
Immobilization: For mild to moderate ankle fractures, immobilization with a cast or a ankle brace may be sufficient. This helps to keep the bones in place, allowing them to heal properly.
Surgery: For severe ankle fractures, surgery may be required to realign and stabilize the bones. Surgery may involve the use of screws, plates, or pins to hold the bones in place.
Pain management: Pain management is an essential aspect of treatment for ankle fractures. Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help relieve pain and reduce swelling.
Physical therapy: Physical therapy is an important part of the recovery process, particularly for more severe ankle fractures. Physical therapy can help improve range of motion, strength, and balance in the ankle, which can reduce the risk of reinjury.
Rest and recovery: Rest and recovery are crucial components of treatment for ankle fractures. Depending on the severity of the fracture, it may take several weeks to several months for the ankle to heal fully. During this time, it is important to avoid activities that can put stress on the ankle and follow the doctor's recommendations for rest and recovery.
In addition to traditional treatment options, there are some newer techniques that may be used to treat ankle fractures, such as minimally invasive surgery and regenerative medicine. Minimally invasive surgery involves making small incisions and using specialized instruments to realign and stabilize the bones, which can reduce recovery times and scarring. Regenerative medicine, such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy, involves injecting the patient's own blood into the affected area to promote healing and reduce inflammation
Ankle fractures can cause significant pain and immobility. Symptoms of an ankle fracture include pain, swelling, tenderness, and bruising around the ankle. Causes of ankle fractures can range from traumatic events to overuse injuries. Treatment for ankle fractures typically involves immobilization, surgery, pain management, physical therapy, and rest and recovery. With proper treatment and rehabilitation, most people with ankle fractures can return to their normal activities.
Tendinitis:
Tendinitis is inflammation of the tendons in the ankle, causing pain and stiffness. Ankle tendinitis is a condition that affects the tendons in the ankle, causing pain and discomfort. It is a common injury among athletes and people who engage in physical activities that involve repetitive ankle movements such as running and jumping.
Symptoms of ankle tendinitis
The most common symptom of ankle tendinitis is pain in the ankle that can range from mild to severe. The pain may be sharp or dull and is usually felt on the inside or outside of the ankle. Other symptoms may include swelling, tenderness, and stiffness in the ankle.
Causes of ankle tendinitis
Ankle tendinitis can be caused by several factors such as overuse, improper footwear, and biomechanical problems. Repetitive stress on the tendons can cause small tears, inflammation, and damage to the tendons. This can happen due to activities such as running, jumping, or walking on uneven surfaces.
Wearing improper footwear, such as shoes with poor support, can also contribute to ankle tendinitis. Biomechanical problems such as flat feet or high arches can also cause ankle tendinitis. These issues can cause an imbalance in the muscles and tendons of the ankle, leading to strain and inflammation.
Treatment for ankle tendinitis
The treatment for ankle tendinitis depends on the severity of the injury. In mild cases, resting the ankle, applying ice, and using anti-inflammatory medication may be enough to relieve the pain and swelling. However, in more severe cases, additional treatment may be required.
Physical therapy can be helpful in treating ankle tendinitis. It can help strengthen the muscles and tendons around the ankle, reducing the strain on the affected tendon. Orthotic devices such as shoe inserts or braces can also be used to provide additional support to the ankle.
In some cases, a doctor may recommend corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation and relieve pain. However, these injections should be used with caution as they can weaken the tendon and increase the risk of further injury.
Surgery may be required in severe cases of ankle tendinitis. Surgery may involve removing damaged tissue, repairing torn tendons, or reconstructing the affected area.
To prevent ankle tendinitis, it is important to wear proper footwear and engage in activities that are appropriate for your fitness level. Stretching before and after exercise can also help reduce the risk of injury. If you have flat feet or high arches, using orthotic devices can help prevent ankle tendinitis.
Ankle tendinitis is a common injury that can cause pain and discomfort. It can be caused by overuse, improper footwear, and biomechanical problems. Treatment for ankle tendinitis includes resting the ankle, physical therapy, orthotic devices, and surgery in severe cases. To prevent ankle tendinitis, it is important to wear proper footwear, engage in appropriate activities, and use orthotic devices if necessary.
Arthritis:
Arthritis is a common cause of ankle pain, especially in older people. It causes inflammation and pain in the joint. Ankle arthritis is a condition that affects the ankle joint, causing pain, inflammation, and stiffness. It is a chronic condition that develops over time and can worsen without proper treatment. In this article, we will explore the symptoms, causes, and treatments for ankle arthritis.
Symptoms of Ankle Arthritis
The symptoms of ankle arthritis vary from person to person, but the most common symptoms include:
Pain in the ankle joint
Stiffness in the ankle joint
Swelling and inflammation in the ankle
Limited range of motion in the ankle joint
Difficulty walking or standing for long periods of time
A clicking or popping sensation in the ankle joint
Bone spurs, which are small bony growths that can develop around the ankle joint
Causes of Ankle Arthritis
Ankle arthritis can be caused by a number of factors, including:
Aging: As we age, the cartilage in our joints can wear down, leading to arthritis.
Genetics: Some people are more prone to developing arthritis due to their genetic makeup.
Injuries: Injuries to the ankle joint, such as fractures or sprains, can increase the risk of developing arthritis later in life.
Overuse: Repeated stress on the ankle joint, such as from running or jumping, can cause arthritis.
Infections: Certain infections can cause arthritis in the ankle joint.
Treatments for Ankle Arthritis
There are several treatments for ankle arthritis, including:
Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. In more severe cases, prescription medications, such as corticosteroids, may be necessary.
Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help to strengthen the muscles around the ankle joint, improve range of motion, and reduce pain.
Bracing or Support Devices: Wearing a brace, ankle sleeve or support device can help to reduce pain and inflammation in the ankle joint.
Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can help to reduce the stress on the ankle joint and reduce pain.
Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or replace the damaged joint.
Prevention of Ankle Arthritis
While it may not be possible to prevent all cases of ankle arthritis, there are some steps you can take to reduce your risk, including:
Maintaining a healthy weight
Wearing proper footwear
Stretching before exercising
Using proper techniques when exercising
Avoiding high-impact activities if you have a history of ankle injuries
Ankle arthritis is a chronic condition that can cause pain, stiffness, and inflammation in the ankle joint. While there is no cure for ankle arthritis, there are several treatments available that can help to reduce pain and improve mobility. If you are experiencing symptoms of ankle arthritis, it is important to consult with your doctor to determine the best course of treatment for your individual needs.
Gout:
Gout is a type of arthritis that causes sudden, severe pain and swelling in the ankle joint. Gout occurs when uric acid builds up in the body, forming crystals that can deposit in joints and other tissues. When gout affects the ankle joint, it can cause severe pain, swelling, and stiffness. In this article, we will explore the symptoms, causes, and treatments for ankle gout.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of ankle gout can be quite painful and can last for days or weeks. They may include:
Intense pain: The pain associated with ankle gout can be sudden and severe, making it difficult to walk or put weight on the affected foot.
Swelling: The ankle joint may become swollen, red, and tender to the touch.
Stiffness: Gout can cause stiffness in the ankle joint, making it difficult to move the foot.
Warmth: The affected area may feel warm to the touch.
Limited range of motion: As the swelling and stiffness increase, the range of motion in the ankle joint may decrease.
Causes:
Gout occurs when there is an excess of uric acid in the blood. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
Genetics: Gout can run in families, making some people more susceptible to the condition than others.
Diet: Consuming foods that are high in purines, such as red meat, seafood, and alcohol, can increase uric acid levels in the blood.
Medications: Certain medications, such as diuretics, can increase uric acid levels in the blood.
Health conditions: Certain health conditions, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and kidney disease, can increase the risk of developing gout.
Treatments:
There are several treatments available for ankle gout, including:
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): These medications can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation in the affected ankle joint.
Colchicine: This medication can help reduce inflammation and prevent future gout attacks.
Corticosteroids: These medications can be injected into the ankle joint to reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
Lifestyle changes: Making changes to your diet and increasing your physical activity can help reduce uric acid levels in the blood and prevent future gout attacks.
Rest and ice: Resting the affected ankle joint and applying ice can help reduce pain and inflammation.
In severe cases of ankle gout, surgery may be necessary to remove the uric acid crystals that have deposited in the joint.
Ankle gout can be a painful and debilitating condition, but there are several treatments available that can help manage the symptoms and prevent future attacks. If you are experiencing symptoms of ankle gout, it is important to speak with your healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment for your specific needs. Additionally, making lifestyle changes, such as reducing your consumption of high-purine foods and increasing your physical activity, can help reduce your risk of developing gout and improve your overall health.
Plantar fasciitis:
Plantar fasciitis is a condition that causes pain in the heel and arch of the foot. It can also cause ankle pain. Plantar fasciitis affects the heel of the foot. It is caused by the inflammation of the plantar fascia, which is a thick band of tissue that runs from the heel to the toes. This condition is most common in people who are overweight, have flat feet, or stand or walk for long periods of time. In this article, we will discuss the symptoms, causes, and treatments for plantar fasciitis.
Symptoms of Plantar Fasciitis
The most common symptom of plantar fasciitis is pain in the heel of the foot. The pain is usually worse in the morning or after a period of rest, such as sitting or standing for a long time. The pain may also be worse after exercise or physical activity. The pain is typically described as a sharp, stabbing sensation in the heel.
Other symptoms of plantar fasciitis may include:
Swelling or redness in the heel
Stiffness in the heel or foot
Pain that worsens over time
Pain that is more severe when standing or walking on hard surfaces
Causes of Plantar Fasciitis
The exact cause of plantar fasciitis is not known, but there are several factors that can increase the risk of developing the condition. These include:
Overuse or strain of the plantar fascia
Flat feet or high arches
Obesity or being overweight
Tight calf muscles or Achilles tendon
Wearing shoes with poor arch support or cushioning
Standing or walking for long periods of time
Treatments for Plantar Fasciitis
There are several treatments for plantar fasciitis, and the most effective treatment will depend on the severity of the condition. Some common treatments include:
Rest and ice: Resting the foot and applying ice can help reduce pain and inflammation.
Physical therapy: Stretching and strengthening exercises can help improve flexibility and reduce the risk of future injury.
Orthotics: Wearing shoe inserts or custom orthotics can help provide support and cushioning to the foot.
Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce pain and inflammation.
Compression: Wearing compression socks or neuropathy socks can help reduce your ankle pain and prevent from further injury.
Injections: Corticosteroid injections can help reduce pain and inflammation in severe cases of plantar fasciitis.
Surgery: Surgery is typically only recommended in severe cases of plantar fasciitis that have not responded to other treatments.
There are several ways to prevent plantar fasciitis, including:
Wearing shoes with good arch support and cushioning
Avoiding high-impact activities that put stress on the feet
Maintaining a healthy weight
Stretching before and after exercise
Avoiding standing or walking for long periods of time
Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that affects the heel of the foot. It is caused by inflammation of the plantar fascia, which can be caused by a number of factors such as overuse or strain, flat feet, or obesity. Symptoms include pain in the heel, stiffness, and swelling. Treatments include rest, physical therapy, orthotics, medications, injections, and surgery. To prevent plantar fasciitis, it is important to wear shoes with good arch support, maintain a healthy weight, and avoid high-impact activities that put stress on the feet.
Bursitis:
Bursitis is the inflammation of the small fluid-filled sacs (bursae) in the ankle, causing pain and swelling. Ankle bursitis is a painful condition that affects the small fluid-filled sacs, called bursae, that cushion and lubricate joints. These sacs are located near the ankle joint and can become inflamed due to a variety of reasons. Bursitis is typically caused by repetitive motions or pressure on the joint, but can also be the result of a traumatic injury or an underlying medical condition.
Symptoms of ankle bursitis may vary depending on the severity of the inflammation. Common symptoms include pain, swelling, stiffness, and redness around the affected area. The pain may be worse with movement, particularly when walking or standing for long periods of time. Some people may also experience a fever or chills if the bursitis is caused by an infection.
The causes of ankle bursitis can vary from person to person. Repetitive motions, such as running or jumping, can cause friction and irritation to the bursae around the ankle joint. Shoes that do not fit properly or provide enough support can also contribute to the development of bursitis. Traumatic injuries, such as ankle sprains or fractures, can also cause bursitis. Certain medical conditions, such as gout, rheumatoid arthritis, and diabetes, can increase the risk of developing bursitis.
The treatment for ankle bursitis depends on the severity of the inflammation and the underlying cause. Resting the affected joint and avoiding activities that aggravate the bursae is often recommended. Applying ice to the affected area can help reduce swelling and relieve pain. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, may also be recommended to help manage pain.
If the bursitis is caused by an infection, antibiotics may be prescribed. In more severe cases, a doctor may recommend draining the fluid from the affected bursa to reduce inflammation. Physical therapy may also be recommended to help improve joint function and prevent future flare-ups.
Preventing ankle bursitis involves taking steps to reduce the risk of injury and inflammation. This includes wearing properly fitting shoes, using protective equipment when engaging in sports or physical activity, and avoiding repetitive motions that strain the ankle joint.
Ankle bursitis is a painful condition that can be caused by a variety of factors. Symptoms include pain, swelling, stiffness, and redness around the affected area. Treatment options include rest, ice, pain relievers, antibiotics, and physical therapy. Preventing bursitis involves taking steps to reduce the risk of injury and inflammation. If you experience symptoms of ankle bursitis, it is important to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Nerve impingement:
Nerve impingement in the ankle can cause sharp pain and weakness in the foot and ankle. Ankle nerve impingement, also known as tarsal tunnel syndrome, is a condition that occurs when the tibial nerve in the ankle becomes compressed or trapped. This can cause a variety of symptoms and can be caused by several different factors.
Symptoms of ankle nerve impingement include pain, numbness, and tingling in the foot and ankle. These symptoms may be felt on the inside of the ankle and foot, as well as in the toes. The pain may be sharp or shooting, and may be worse at night or after prolonged standing or walking.
The causes of ankle nerve impingement can vary. The most common cause is overuse or repetitive stress on the ankle and foot, such as running or walking on hard surfaces. Other causes may include arthritis, bone spurs, flat feet, or an injury to the ankle or foot.
Treatments for ankle nerve impingement depend on the severity of the condition and the underlying cause. Conservative treatments may include rest, ice, compression, and elevation of the affected foot, as well as physical therapy to strengthen the muscles in the ankle and foot.
In some cases, medication may be prescribed to relieve pain and inflammation. This may include over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription medications such as corticosteroids.
If conservative treatments are not effective, surgery may be necessary. This may involve releasing the tibial nerve from any structures that are compressing it, or removing any bone spurs that may be causing the impingement.
Prevention of ankle nerve impingement involves taking steps to reduce the risk of injury or overuse. This may include wearing appropriate footwear, avoiding high-impact activities that put stress on the ankle and foot, and maintaining a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the joints.
Ankle nerve impingement can cause a range of symptoms and can be caused by various factors. Treatment options depend on the severity of the condition, and prevention involves taking steps to reduce the risk of injury or overuse. If you are experiencing symptoms of ankle nerve impingement, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Overuse injuries:
Overuse injuries such as tendinitis, stress fractures, and bursitis can occur due to repetitive movements in the ankle. Ankle overuse injuries refer to pain and discomfort caused by repetitive or prolonged movements that strain the ankle joint, tendons, and ligaments. These injuries commonly affect athletes, dancers, and people who engage in activities that require frequent jumping, running, or twisting.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of ankle overuse injuries may include pain, stiffness, swelling, tenderness, and a reduced range of motion. These symptoms may worsen with activity and improve with rest. In severe cases, the ankle may become unstable, and the person may have difficulty standing or walking.
Causes:
Ankle overuse injuries are typically caused by repetitive or prolonged activities that put excessive stress on the ankle joint, tendons, and ligaments. These activities may include running, jumping, dancing, or playing sports such as basketball, soccer, and tennis. Other factors that can contribute to ankle overuse injuries include poor footwear, weak ankle muscles, and previous ankle injuries.
Treatments:
The treatment for ankle overuse injuries may include rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) therapy to reduce swelling and pain. Additionally, a person may need to modify their activities or take a break from the activities that caused the injury. In some cases, physical therapy may be necessary to strengthen the ankle muscles, improve flexibility, and promote healing.
Medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be used to reduce pain and inflammation. A doctor may also recommend the use of ankle braces or supports to provide additional stability to the ankle joint during activities.
In rare cases, surgery may be necessary to repair a severely damaged tendon or ligament. However, surgery is typically reserved for cases where other treatments have failed, and the injury is significantly affecting a person's daily activities.
Prevention:
To prevent ankle overuse injuries, it is essential to take measures to reduce the stress on the ankle joint during activities. These measures may include wearing proper footwear, gradually increasing the intensity and duration of activities, warming up before exercise, and incorporating strength and flexibility exercises into a fitness routine.
Ankle overuse injuries are a common type of injury that can cause pain and discomfort. They are typically caused by repetitive or prolonged activities that put excessive stress on the ankle joint, tendons, and ligaments. Treatment for these injuries typically involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) therapy, physical therapy, and medication. With proper prevention measures, ankle overuse injuries can be prevented, and individuals can continue to engage in the activities they enjoy without discomfort or pain.
Ankle instability:
Ankle instability can cause pain, swelling and weakness in the ankle, especially when the ligaments have been damaged. Ankle instability is a condition that occurs when the ankle joint is not stable and has a tendency to give way or twist. It can occur after an ankle sprain, trauma or repetitive injuries. Ankle instability can be a serious condition, and if left untreated, it can cause long-term pain, discomfort and disability.
Symptoms
The symptoms of ankle instability may vary from person to person, and the severity of the symptoms depends on the degree of instability in the ankle joint. Some of the common symptoms of ankle instability include:
Frequent ankle sprains
Pain or discomfort in the ankle joint
Swelling and stiffness in the ankle joint
Weakness or instability in the ankle joint
A sensation of the ankle giving way or twisting
Difficulty in walking or running
Tenderness on the outer side of the ankle
Ankle instability can be caused by a number of factors, including:
Ankle sprains: This is the most common cause of ankle instability. When the ligaments in the ankle joint are stretched or torn, it can cause instability in the ankle joint.
Trauma: A sudden impact or injury to the ankle joint can damage the ligaments and cause ankle instability.
Overuse: Repetitive stress on the ankle joint due to activities like running or jumping can cause instability in the ankle joint.
Genetics: Some people may have a genetic predisposition to ankle instability.
Treatments
The treatment for ankle instability depends on the severity of the condition. Mild cases of ankle instability can be treated with rest, ice, compression and elevation (RICE). This helps to reduce swelling and inflammation in the ankle joint. Physical therapy can also be helpful to strengthen the muscles around the ankle joint and improve stability.
In more severe cases, ankle bracing or taping may be necessary to provide additional support to the ankle joint. Surgery may also be necessary in cases of severe ankle instability, where the ligaments in the ankle joint are severely damaged or torn.
Preventing ankle instability involves taking precautions to avoid ankle sprains or injuries. This can be done by:
Wearing proper footwear that provides support to the ankle joint
Stretching and warming up before physical activity
Wearing a lace-up ankle brace can support your ankle and reduce risk of injury.
Avoiding activities that put excessive stress on the ankle joint
Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce stress on the ankle joint
In conclusion, ankle instability is a condition that can cause long-term pain and discomfort if left untreated. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms of ankle instability. With proper treatment and precautions, ankle instability can be managed effectively, and you can resume your normal activities without any pain or discomfort.
Our orthopedic braces can be extremely effective in relieving pain for many different types of injuries and conditions. By providing targeted support and compression to the affected area, braces can help to reduce inflammation, improve circulation, and stabilize the joint or muscle, all of which can help to alleviate pain and improve overall mobility. Whether a customer is dealing with a chronic condition like arthritis or has recently suffered an injury like a sprained ankle or torn ligament, a well-designed orthopedic brace can provide the comfort and support they need to get back to their daily activities with less pain and discomfort.